Unified Pricing Management Key Components and Concepts
Important: If you are considering migrating your ERP to Unified pricing management, please contact your Sana representative before making any changes. We want to ensure a smooth transition by working with you on an individualized plan tailored to your business needs.
In Unified pricing management, several key components and concepts work together to create flexible and dynamic pricing strategies.
Key Concepts
-
Price attributes: Price attributes give you a flexible way to define your pricing factors. They leverage information from customers, products, sales order headers, and sales order lines. Since price attributes integrate with the customer and product attribute framework, they offer high configurability.
-
Price component codes: Price component codes categorize price attributes into distinct groups. They serve as the fundamental elements of your pricing structure. When setting up a price and discount rule, you also associate it with a specific price component code.
-
Price structures: Price structures define the order and flow of your price component codes. You can apply a single price structure across your entire company or use different structures for various order attributes within a company. The price determination logic built into the price structure ensures the base price can be determined. This base price is the initial price before any adjustments are applied (Base price + Price adjustment = Selling price).
-
Concurrency modes: Concurrency modes dictate how the final price is determined when multiple pricing rules are linked to the same price component code. They control the interaction between these rules to ensure the correct pricing is applied.
-
Price groups: Price groups are used to organize and categorize pricing data based on shared characteristics or conditions. They allow businesses to apply consistent pricing rules to a set of products, customers, or other relevant attributes. Price groups simplify the management of pricing across different segments or categories, ensuring that the correct pricing structures and rules are applied efficiently.
Key Price Components
-
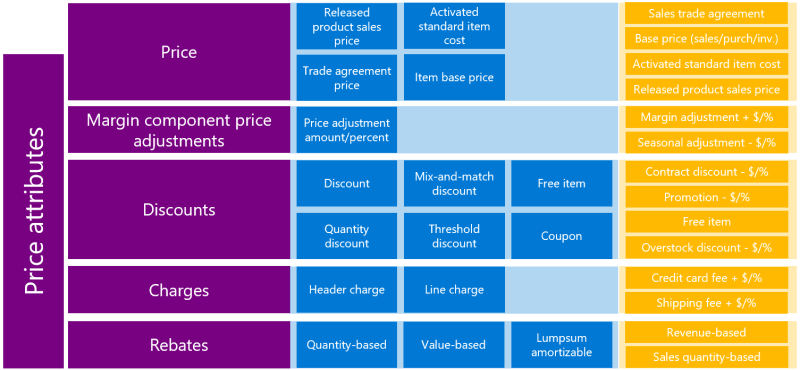
Price: The price is the core component of any pricing strategy and refers to the base price of a product or service before any adjustments, discounts, or additional charges are applied. The price can be sourced from the trade agreement and if the trade agreement does not exist, then the base price is applied. The base price can be derived from the purchase or the standard cost of a product, or default price specified in the product master.
-
Margin component price adjustment: The margin component price adjustment allows businesses to modify the base price to ensure desired profit margins are met. The margin component price adjustment enables price modifications to be made at the time of the order before any discounts or charges are applied.
-
Discounts: Discounts are reductions applied to the base price or total transaction value to encourage sales, reward customer loyalty, or incentivize bulk purchases. Discounts can be defined as a percentage or fixed amount, and they can be conditional based on predefined criteria, such as purchase quantity or promotional events. Pricing management includes various types of discounts, such as simple discounts, quantity discounts, mix and match discounts, threshold discounts, free items, and other features like coupons, funds, and claims.
-
Charges: Charges refer to additional fees that are added to the base price of a product or service. These can include things like shipping costs, handling fees, or service charges. Charges can be applied at the header level or the order line level.
-
Rebates: Rebates are price adjustments that are provided after the sale has been completed. They are typically based on the fulfillment of certain conditions, such as achieving a specific purchase volume, completing a contract term, or meeting a predefined sales target. Rebates are applied retrospectively, meaning that the customer is refunded or credited after the transaction has been processed.
Image Source: Microsoft
In the next articles, we will explore these components and concepts in more detail to provide a deeper understanding of how they work together to create a comprehensive pricing strategy. For users seeking more information on components and concepts not covered in our documentation or that we don't provide in-depth details about, we recommend referring to the official Microsoft documentation for further insights and guidance.
For more information, refer to the official Microsoft documentation: Unified Pricing Management.